SECTION A
1. A small amount of ethanol was added to a large amount of water and the mixture shaken.
(a) State what was observed.
(b) In the mixture in (a), state which one of the components is the
(i) Solute.
(ii) Solvent.
(c) Name the method that would be used to separate the mixture formed in (a).
(d) In another experiment, simsim oil was shaken with water.
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (d) (i).
(iii) Name the piece of apparatus that would be used to separate the mixture.
2. The atomic number of elements Q, R and T are 6, 17 and 19 respectively.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of
(i) Q
(ii) R
(iii) T
(b) R reacted separately with Q and T to form compounds X and Y respectively. State the type of bond that exists in compound
(i) X
(ii) Y
(c) Identify which one of the compounds in (b) would be soluble in
(i) Water.
(ii) Petrol.
3. (a) Sodium metal was burn in excess oxygen.
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction that took place.
(b) Water was added to the product in (a).
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Write equation for the reaction that took place.
4. (a) A mixture of magnesium powder and lead (II) oxide was heated strongly until there was no further change.
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Write equation for the reaction that took place.
(b) The experiment in (a) was repeated using a mixture of copper turning and magnesium oxide. State what was observed.
(c) Briefly explain your observation in (a) and (b).
5. (a) Natural rubber is soft and it is normally made hard before use.
(i) Name one process by which natural rubber is made hard.
(ii) State how natural rubber is made hard by the process you have named in (a) (i).
(b) State
(i) two reasons why natural rubber is made hard before use.
(ii) two uses of rubber.
6. (a) (i) Write equation to show how hydrogen can be prepared using zinc and dilute sulphuric acid.
(ii) State how hydrogen can be tested in laboratory.
(b) Hydrogen reacts with copper (II) oxide according to the following equation:
CuO(s) + H2(g) ———→ Cu(s) + H2O(l)
(i) State what is observed when dry hydrogen is passed over heated copper (II) oxide.
(ii) Calculate the volume of hydrogen at s.t.p, that would react with copper (II) oxide to form 3.20 g of copper.
(O=16; Cu=64; One mole of a gas occupies 22.4 dm3 at s.t.p.)
7. (a) When a nitrate of a metal Y was heated strongly, brown fumes were observed together with a solid residue which was reddish drown when hot and yellow when cooled.
(i) Identify Y.
(ii) Write equation for the reaction that took place.
(b) The residue from (a) was heated with dilute nitric acid. Write equation for the reaction that took place.
(c) To the product in (b), dilute sodium hydroxide was added dropwise until there was no further change. State what was observed.
8. (a) Carbon monoxide was passed over heated iron (II) oxide.
(i) Write equation for the reaction that took place.
(ii) Write equation for the reaction between the solid produced in (a) (i) and dilute sulphuric acid.
(b) Chlorine was bubbled through the product in (a) (i).
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Write ionic equation for the reaction that took place.
9. (a) Write equation for the complete combustion of methane.
(b) 0.12 dm3 of methane was completely burnt in air. Calculate the
(i) volume of oxygen at s.t.p that would be required for the complete combustion of methane.
(ii) quantity of heat that would be liberated during the reaction.
( One mole of methane completely burns to give 890 kJ of heat; One mole of gas occupies 22.4 cm3 at s.t.p).
10. (a) Both copper wire and copper (II) sulphate conduct electric current. Name the particles which conduct electric current in
(i) Copper wire
(ii) Aqueous copper (ii) sulphate.
(b) T he set of apparatus in the diagram below was used to find out what happens when electrolyte is connected to a source of electric current.
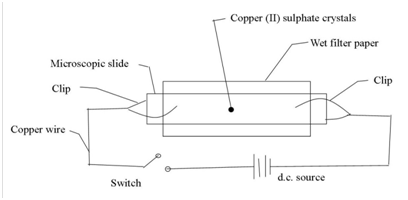
State what was observed
(i) When the switch was closed.
(ii) If copper (II) sulphate crystal was rep laced with potassium manganite (VI) crystal and the switch closed once again.
(c) (i) Give a eason for the observation you have made in (b) (i) and (ii)
(ii) State any general conclusion that can be drawn following the reason you have given in (c) (i).
SECTION B
11. (a) (i) With the aid of a labeled diagram, explain how a pure dry sample of sulphur dioxide can be prepared in the laboratory using sodium sulpite and sulphuric acid.
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction leading to the formation of sulphur dioxide.
(b) Name one reagent that would be used to confirm the presence of sulphur dioxide, and state what would be observed if the reagent you have named was treated with sulphur dioxide.
(c) Write an equation to show the reaction between sulphur dioxide and
(i) water
(ii) oxygen in the presence of hot platinum.
(d) The product of the reaction in (c) (ii) as mixed with water and barium nitrate solution added to the resultant mixture.
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Explain what took place. (No equation required)
12. (a) State the difference between the following pairs of terms.
(i) Synthetic polymer and natural polymer.
(ii) Thermosetting polymer and thermo softening (or thermoplastic) polymer.
(b) (i) State the conditions under which sulphurc acid can react with ethanol to produce ethane.
(ii) Write an equation leading to the formation of ethane.
(c) When reacted together, ethene molecules can form a polymer.
(i) Name the polymer.
(ii) Write an equation leading to the formatin of the poymer.
(iii) State one use of the polymer.
(d) Name one
(i) Synthetic polymer other than the one you have named in (c)
(ii) Natural polymer other than rubber.
(e) State one
(i) Use of each of the polymers you have named in (d)
(ii) Disadvantage of the polymer formed in (c) (ii).
13. (a) Chlorine can be prepared n the laboratory using potassium manganite (VI), KMnO4.
(i) Name one substance that reacts with potassium manganite (VII) to produce chlorine.
(ii) State the condition for the reaction.
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction leading to the formation of chlorine.
(b) Damp blue litmus paper was dropped in a gas jar containing chlorine. State what was observed and explain your observation(s)
(c) A boiling tube filled with chlorine water and exposed to sunlight for some time.
(i) State what was observed.
(ii) Explain with the aid of equation(s), your observation(s) in (c) (i).
(d) Write an equation to show how chlorine can react with
(i) dilute potassium hydroxide solution.
(ii) Turpentine, C10H16
(e) Briefly describe a test you would carry out to confirm the presence of chloride ion in solution; State what would be observed and write an equation for the reaction that would take place.
14. (a) Write an equation for the reaction between oxygen and
(i) Ammonia in the presence of heated platinum.
(ii) Nitrogen monoxide.
(b) State how the product in (a) (ii) can be converted to nitric acid.
(c) Write an equation and state the conditions for the reaction between nitric acid and
(i) sulphur
(ii) lead (II) oxide
(d) In each case, state what was observed and write an equation for the reaction that took place when, sodium nitrate was heated strongly
(i) alone
(ii) as a mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid
END
