- Which of the following parts of the human ear is responsible for stability of the body?
- Cochlea.
- Round window.
- Eustachian tube.
- Semi-circular canals.
- A person of blood group AB receives blood from any donor because the recipient
- Lacks antibodies a and b.
- Has antigen A and antibody b.
- Lacks antigens A and B.
- Has both antibodies a and b.
- Which of the following mineral combinations would most affect leaf development when deficient?
- Copper and silicon.
- Nitrogen and magnesium.
- Calcium and copper.
- Manganese and phosphorus.
- Which one of the following is the least important benefit of seed and fruit dispersal to plant?
- Increasing changes of finding better habitant for multiplication.
- Avoiding being eaten by animals in its original habitant.
- Reducing competition for food resulting from overcrowding.
- Ensuring colonization of different habitants.
- The role of the dilute hydrochloric acid added to a solution when testing for non – reducing sugar is to
- Neutralize the solution.
- Provide a suitable medium for the action of Benedict’s reagent.
- Hydrolyze the non – reducing sugars.
- Kill the bacteria in the test solution.
- Which one of the following is not an adaptation of plants to reduce water looss?
- Fewer and smaller leaves.
- Leaves reduced to spines.
- Rolled up leaves.
- Alternate leaf arrangement.
- Which of the following responses of the body occur at the same time due to over heating?
- Vasodilation and reduction in metabolic rate.
- Vasoconstriction and raising of the hair.
- Vasoconstriction and shivering.
- Raising of the hair and shivering.
- A sample of soil was poured into a measuring cylinder containing water and the mixture stirred. The readings taken were as follow: Volume of water in the measuring cylinder = 215 cm3.Volume of water + soil = 260 cm3.Volume of water + soil after stirring = 250 cm3.What was the percentage of air in the soil?
- 10
- 22
- 35
- 45
9. Which one of the following hormones stimulates the production of progesterone from the corpus luteum?
A. Testosterone.
B. Luteinizing hormone.
C. Oestrogen.
D. Follicle stimulating hormone.
10. Which one of the following systems is well developed in a tapeworm?
A. Digestive system.
B. Nervous system.
C. Reproductive system.
D. Respiratory system.
11. In humans, the gene for brown eyes B is dominant to the gene for blueeyes b. if a heterozygous brown eyed male married a blue eyed female, what is the probability of producing blue eyed offspring?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
12. Which one of the following statements is true, when testing a leaf for starch?
A. Placing the leaf in water removes chlorophyll.
B. Boiling the leaf in water allows penetration of iodine.
C. Dipping the leaf in cold water softens it.
D. Boiling the leaf in the leaf in methylated spirit dissolves chlorophyll.
13. Which one of the following phyla consists of human parasites?
A. Nematode.
B. Mollusca.
C. Coelentera
D. Echinodermata.
14. Which one of the following is not used for gaseous exchange in amphibians?
A. Lungs.
B. Skin.
C. Mouth.
D. Nostrils.
15. Prolonged anaerobic respiration in plants in plants is not good becaouse
A. So much energy is lost.
B. An oxygen debt is incurred.
C. Ethanol produced becomes poisonous.
D. Much carbon dioxide is produced.
16. Insects’ blood lacks hemoglobin because
A. Oxygen diffuses through the body surface.
B. Respiratory gases are transported in the tracheole system
C. Oxygen is transported by a different pigment
D. They posses very narrow vessels
17. A reason for simpler excretory organs in plants as compared to those in animals is that plants.
A. Do not excrete solid wastes.
B. Have lower metabolic rates.
C. Do not use proteins.
D. Are primary producers.
18. The main advantages of biological control of pests over the use of pesticides is that it
A. Does not pollute the environment.
B. Is cheaper.
C. Has a longer lasting effect.
D. Is non-discriminatory.
19. The most effective method of contraction in a human male is
A. Vasectomy.
B. Tubal ligation.
C. Withdrawal.
D. Condom use.
20. Which one of the following occurs when internal intercostal muscles contract during breathing?
A. Thoracic volume increases.
B. Ribs are raised.
C. Inhalation occurs.
D. Thoracic pressure increases.
21. The opening of stomata during night and closure during day is an attempt to
A. Stop gaseous exchange.
B. Conserve water.
C. Conserve energy.
D. Lower the temperature.
22. Production of many pollen grains is an adaptation for
A. Cross pollination.
B. Insect pollination.
C. Wind pollination.
D. Self pollination.
23. Figure 1 shows a food web in a terrestrial ecosystem.
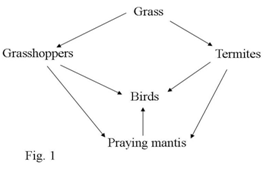
Which one of the following would occur if the praying mantis were removed from the ecosystem?
A. Decrease in number of grass hoppers.
B. Increase in number of birds.
C. Decrease in amount of grass.
D. Decrease in number of termites.
1. 24. The most effective method of contraction in a human male is
A. Vasectomy.
B. Tubal ligation.
C. Withdrawal.
D. Condom use.
2. 25. Which one of the following occurs when internal intercostal muscles contract during breathing?
A. Thoracic volume increases.
B. Ribs are raised.
C. Inhalation occurs.
D. Thoracic pressure increases.
3. 26.The opening of stomata during night and closure during day is an attempt to
A. Stop gaseous exchange.
B. Conserve water.
C. Conserve energy.
D. Lower the temperature.
4. 27. Production of many pollen grains is an adaptation for
A. Cross pollination.
B. Insect pollination.
C. Wind pollination.
D. Self pollination.
5. 28. Which one of the following hormones is most likely to be secreted in an individual as a result of not eating food for a day?
A. Insulin.
B. Glucagon.
C. Thyroxine.
D. Adrenaline
6. 29. A bird’s egg is larger then an ovum of an elephant because more
A. Food reserves are needed for external development.
B. Space is needed for storing wastes.
C. Space is required for conservation oxygen.
D. Space is required for gaseous exchange.
7. 30. Which one of the following is a defect of blurred vision of near objects and the corrective lens to the defect?
A. Short sightedness, concave lens.
B. Long sightedness, concave lens.
C. Long sightedness, convex lens.
D. Short sightedness, convex lens.
8. 31. When 2 g of food substance was burnt completely, the heat produced raised the temperature of 50 cm 3 of water from 25oC to 37oC. (Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg-1K-1). The energy content of the food substance in Jg-1 is
A. 2520
B. 12602
C. 252
D. 126
9. 32. The pappus on the fruit in figure 2 are remains of the
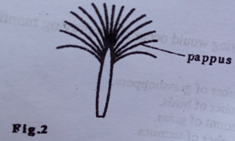
A. Petals.
B. Pericarp.
C. Semen.
D. Calyx.
1. 33. To which one of the following bones is biceps muscle attached?
A. Clavicle.
B. Radius.
C. Humerus.
D. Ulna.
2. 34.Figure 3 in an experimental set on germinating seed.
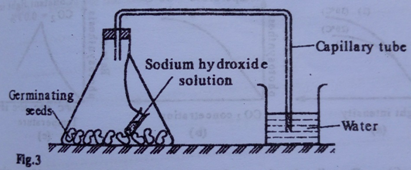
Which one of the following will be observed after three days of the experiment?
A. Water will turn milky.
B. Water level in the tube will drop.
C. Germinating seeds will rot.
D. Water level in the tube will rise.
3. 35. (a) Figure 4 (a), (b) and (c) show the variation of rate of photosynthesis under different conditions. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow.

(a) (i) Describe the shape of curve 1 in figure 4 (a).
(i) Giving a reason, state why the rate of photosynthesis in curve 1 of figure 4 (a) remains constant at some stage.
(b) Giving a reason state two factors which might be the cause of a contact rate of photosynthesis in figure 4 (b).
(c) Describe the shape of the curve in figure 4 (c).
(d) (i) From figure (a), (b) and (c), state factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis.
(ii) Explain how each of the factors stated in (i) affect the rate of photosynthesis
4. 36. Explain how each of the following features in a mammal affects body temperature,
(a) Size of the animal
(b) Hair/fur on the skin
(c) Fat under the skin
(d) Why is it important to maintain a constant body temperature?
5. 37. The table below shows the composition of blood of three adult individuals. One lives at a high altitude, another is anemic and the other has an infection. It also shows the average number of each blood component in an adult human. Study the information in the table and answer the questions that follow.
|
Component of blood |
Person A |
Person B |
Person C |
Average number in adult human |
|
Red blood cells mm3 |
7,500,000 |
5,000,000 |
2,000,000 |
5,000,000 |
|
White blood cells mm3 |
6,000 |
8,000 |
12,000 |
5,000-10,000 |
|
Blood platelets per mm3 |
250,000 |
255,000 |
100,000 |
250,000 |
(a) Giving a reason, suggest the person,
(i) Who lives at high altitudes
(ii) Who is anaemic
(iii) Who has an infection
(b) Suggest a likely effect of the observed number of blood platelets in person C.
6. 38. (a) Describe how the amount of water in the human body is regulated.
(b) How does the human body restore a low level of glucose in the blood to normal levels?
7. 39.Using suitable examples, describe how new plants are formed by asexual reproduction.
8. 40.Describe an experiment to determine the percentage of air in a soil sample.
9. 41.(a) Describe inhalation and exhalation in a bony fish.
(c) How is the respiratory surface in fish adapted for its function?
1. Which one of the following hormones stimulates the production of progesterone from the corpus luteum?
A. Testosterone.
B. Luteinizing hormone.
C. Oestrogen.
D. Follicle stimulating hormone.
2. Which one of the following systems is well developed in a tapeworm?
A. Digestive system.
B. Nervous system.
C. Reproductive system.
D. Respiratory system.
3. In humans, the gene for brown eyes B is dominant to the gene for blueeyes b. if a heterozygous brown eyed male married a blue eyed female, what is the probability of producing blue eyed offspring?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
4. Which one of the following statements is true, when testing a leaf for starch?
A. Placing the leaf in water removes chlorophyll.
B. Boiling the leaf in water allows penetration of iodine.
C. Dipping the leaf in cold water softens it.
D. Boiling the leaf in the leaf in methylated spirit dissolves chlorophyll.
5. Which one of the following phyla consists of human parasites?
A. Nematode.
B. Mollusca.
C. Coelentera
D. Echinodermata.
6. Which one of the following is not used for gaseous exchange in amphibians?
A. Lungs.
B. Skin.
C. Mouth.
D. Nostrils.
7. Prolonged anaerobic respiration in plants in plants is not good becaouse
A. So much energy is lost.
B. An oxygen debt is incurred.
C. Ethanol produced becomes poisonous.
D. Much carbon dioxide is produced.
8. Insects’ blood lacks hemoglobin because
A. Oxygen diffuses through the body surface.
B. Respiratory gases are transported in the tracheole system
C. Oxygen is transported by a different pigment
D. They posses very narrow vessels
9. A reason for simpler excretory organs in plants as compared to those in animals is that plants.
A. Do not excrete solid wastes.
B. Have lower metabolic rates.
C. Do not use proteins.
D. Are primary producers.
10. The main advantages of biological control of pests over the use of pesticides is that it
A. Does not pollute the environment.
B. Is cheaper.
C. Has a longer lasting effect.
D. Is non-discriminatory.
11. The most effective method of contraction in a human male is
A. Vasectomy.
B. Tubal ligation.
C. Withdrawal.
D. Condom use.
12. Which one of the following occurs when internal intercostal muscles contract during breathing?
A. Thoracic volume increases.
B. Ribs are raised.
C. Inhalation occurs.
D. Thoracic pressure increases.
13. The opening of stomata during night and closure during day is an attempt to
A. Stop gaseous exchange.
B. Conserve water.
C. Conserve energy.
D. Lower the temperature.
14. Production of many pollen grains is an adaptation for
A. Cross pollination.
B. Insect pollination.
C. Wind pollination.
D. Self pollination.
15. Figure 1 shows a food web in a terrestrial ecosystem.
