1. a) A metallic element T reacts with nitrogen to form a compound with the formula T3N2
i) State the valency of T.
ii) Write equation for the reaction between T andchlorine
b) 3.2g of T reacted completely with 600cm3 of nitrogen at s.t.p. Determine the atomic mass of T(1 mole of a gas occupies 22.4dm3;T reacts with nitrogen in the ratio 3:1)
2. a) Write the chemical name of rust
b) State the conditions necessary for rusting to occur
c) Figure 1 shows a set-up of apparatus that was used to investigate a condition necessary for iron nails to rust.
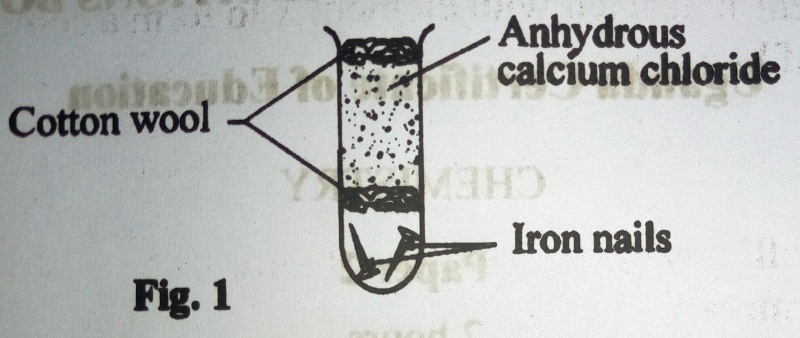
State the condition that was being investigated.
d) State;
i) one disadvantage of rust
ii) one method of preventing rusting
3. Table below shows the mass numbers and atomic numbers of elements W, X and Y. Study the table and answer the questions that follow
|
Element |
Mass number |
Atomic number |
|
W |
24 |
12 |
|
X |
14 |
7 |
|
Y |
39 |
19 |
a) State the number of;
i) electrons in the atom of element Y
ii) neutrons in the atom of element Y
b) Write the electronic configuration of the ion that can be formed by the atom of element Y
c) Identify the group in the Periodic Table to which element X belongs
d) Element W reacted with element X to form a compound Z. State the type of bond in Z.
4. The set up of the apparatus in figure 2 was used for electrolyzing silver nitrate solution
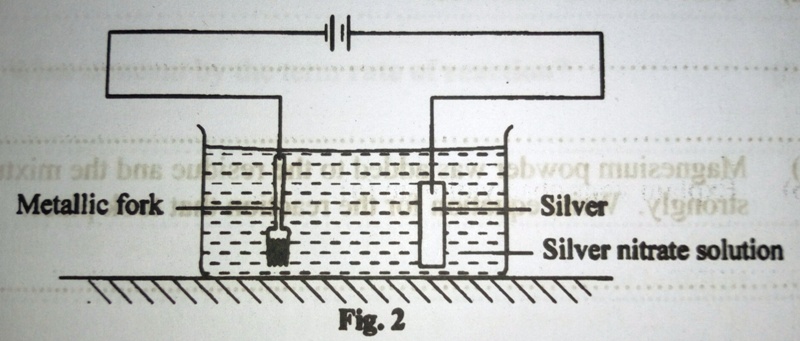
a) State what was observed on the;
i) metallic fork
ii) silver
b) Write equation for the reaction that took place at the;
i) electrode with the fork
ii) electrode with silver
c) i) Name the process taking place at the electrode with the fork
ii) State one use of the process in (c) (i)
5. Clean zinc granules were added to a solution of copper(II) sulphate.
a) State what was observed
b) Explain your observation in (a)
c) Write equation to support your answer in (b)
6. Ammonium sulphate dissolves in water according to the following equation:
- (NH4)2SO4(s) + 2H2O(l) à 2NH4OH(aq)+ H2SO4(aq)
a) State what would be observed if aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate was added to the resultant solution
b) Briefly explain your answer above.
7.Lead(II)carbonate was heated until there was no further change.
a) State what was observed
b) Magnesium powder was added to the residue and the mixture heated strongly. Write equation for the reaction that took place.
c) The experiment in (b) was repeated using copper turning instead of magnesium powder.
i) State what was observed
ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i)
8. When ammonium chloride was mixed with potassium hydroxide and the mixture heated strongly, ammonia was evolved
a) Write equation for the reaction leading to the formation of ammonia
b) Ammonia was bubbled through zinc sulphate solution until there was no further change.
i) State what was observed
ii) Give reason(s) for your observation(s) in (b) (i)
9.a) What is meant by the term rate of reaction?
b) During an experiment to determine the rate of production of carbon dioxide from calcium carbonate at room temperature, the volume of carbon dioxide varied with time as shown in the graph in figure 3

Show how the rate the reaction at timeT can be determined
c) State two factors other than temperature that can affect the rate of a reaction
10.a) Write equation for the complete combustion of carbon
b) If 80kg of charcoal cost UGX 20,000. Calculate the cost of charcoal required to produce 163,750kJ of heat energy.
(C=12; The enthalpy of combustion of carbon = -393kJmol-1)
c) State one use of charcoal other than fuel
11.a) Differntiate between miscible and immiscible liquids
b) i) Name two compounds that can form miscible liquid mixture and draw a diagram for the set-up of apparatus that can be used to separate the mixture
ii) State onemethod that can be used to determine the purity of the components of the mixture in (b)(i)
c) Table below shows variation in temperature with time when a solid X was heated to boiling.
|
Temperature(0C) |
25 |
47 |
80 |
80 |
162 |
218 |
218 |
|
Time (minutes) |
0 |
1.0 |
2.5 |
4.5 |
7.0 |
8.7 |
9.5 |
i) Draw a graph of temperature against time
ii) Explain the shape of the graph
12. a) Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by oxidation of concentrated hydrochloric acid
i) Name one suitable substance that can be used for oxidizing hydrochloric acid
ii) Outline how a pure dry sample of chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory from the above reaction.
b) State and write equation(s) to show how phosphorous reacts with chlorine.
c) Explain the reaction of chlorine with potassium bromide
13. a) i) State two ways which water bodies can be polluted
ii) Describe how polluted water can be treated on a large scale so that it is safe for use.
b) When soap solution was added to a sample of water, a white precipitat was formed. But when the soap solution was added to another portion of the water that had been boiled, no precipitation took place. Explain. (Include equation where possible)
14.a) Using equations only, outline the processes involved in the manufacture of nitric acid.
b) A mixture of concentrated nitric acid and sulphur was warmed.
i) State what was observed
ii) Write equation for the reaction that took place
c) Ammonium nitrate is among the most widely used fertilizers. Write equation for the reaction leading to the formation of ammonium nitrate from nitric acid.
d) Ammonium nitrate dissolves in water according to the following equation:
NH4NO3(s) + H2O(l) à HNO3(aq) + NH4OH(aq)
Excessive use of ammonium nitrate as a fertilizer can cause the soil to become acidic. Explain
d) Write equation to show the effect of heat on;
i) silver nitrate
ii) potassium nitrate
f) State one use of nitric acid other than in the manufacture of fertlisers.
