PAPER 1
THEORY
SECTION A
Answer all questions in the section. For each question select the most correct option and write the letter representing it in the box provided.
1. Individuals with blood AB are said to be universal recipients because they have
A. No antigens.
B. No antibodies.
C. Both antigens and antibodies.
D. Antibodies a and b
2. Which one of the following is true about the nervous system of a mammal?
A. Cell bodies of the sensory neurons are found in the ganglia.
B. Cell bodies of the sensory neurons are found in the grey matter.
C. Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the central nervous system to receptors.
D. Cell bodies of sensory neurons are found in the receptors.
3. The last segment of a caterpillar bears a pair of structures called
A. Prologs.
B. Ovipositors.
C. Claspers.
D. True legs.
4. In cattle the gene for red coat color, R, is co-dominant to that for white coat color, W. if a red cow mated to a white bull, what would be the phenotype of the F1 generation?
A. All red
B. All white
C. 3 red: 1 white
D. Intermediate coat color (roan)
5. What are the products of the hydrolysis of lactose?
A. Galactose and fructose.
B. Glucose and Galactose.
C. Glucose only
D. Glucose and fructose.
6. Photosynthesis is said to have a pair of raw materials, a pair of conditions, and a pair of products. Which of these is the correct set?
A. Carbon dioxide and light; water and chlorophyll; oxygen and sugars.
B. Water and light; carbon dioxide and chlorophyll; oxygen and sugars.
C. Light and chlorophyll; carbon dioxide and sugar; water and oxygen.
D. Carbon dioxide and water; light and chlorophyll; oxygen and sugars.
7. Which one of the following controls the activities of other ductless glands?
A. Thyroid
B. Adrenal
C. Pituitary
D. Islets of langerhans
8. A runner is a
A. Stem which bends over and roots in the soil.
B. Horizontal stem above the ground which gives roots and aerial shoots at the nodes.
C. Horizontal stem beneath the ground which gives rise to roots and aerial shoots at the nodes.
D. Short vertical stem buds beneath the soil.
9. What would result if secretion of gastric juice were inhibited in an individual who has just had a meal of posho and beans?
A. The person would suffer from heartburn.
B. The person would suffer from constipation.
C. Digestion would not take place.
D. Digestion of certain food types would be delayed.
10. Which of the following is true about arteries? They
A. Carry blood away from the heart.
B. Carry deoxygenated blood.
C. Carry oxygenated blood.
D. Possess valves along their length.
11. Which of the following is true about nastic response?
A. Depends on the direction of the stimulus.
B. Does not involve hormones.
C. It is relative slow.
D. Does not involve only growth.
12. Urine is formed by
A. Ultra filtration and selective reabsorption.
B. Selective reabsorption in the proximal tubule.
C. Selective reabsorption at the loop of Henley.
D. Ultra filtration in the Bowman's capsule.
13. Which one of the following substances accumulates in muscles during vigorous exercise?
A. Water
B. Lactic acid
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Oxygen
14. The best method of measuring the growth rate of a seedling is by
A. Taking records of dry weight.
B. Measuring the fresh weight.
C. Observing the increase in volume.
D. Observing the increase in the size of the leaves.
15. Which one of these methods is not important in the maintenance of soil fertility on a given piece of land?
A. Practicing crop rotation.
B. Addition of organic manure
C. Maintaining of vegetation cover.
D. Burning of the grass in the plot regularly.
16. Short sightedness is caused by the
A. Lens becoming thicker.
B. Suspensory ligament becoming shorter.
C. Contraction of the cilliary muscles.
D. Expansion of iris muscles.
17. Which one of the following soil types has the highest capillarity?
A. Silt
B. Loam
C. Clay
D. Sand
18. When blood passes from the lungs to the kidney it has to go through the
A. Pulmonary artery, tricuspid valve and aorta.
B. Pulmonary vein, bicuspid valve and aorta.
C. Anterior venacava, tricuspid valve and aorta.
D. Posterior venacava, bicuspid valve and aorta.
19. 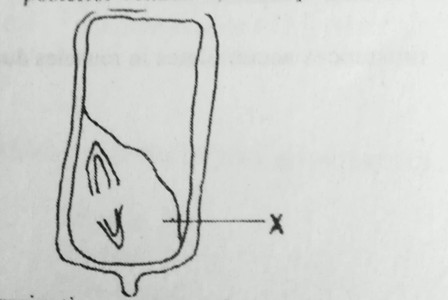
In a germinating grain, the function of X is to
A. Absorb food from the endosperm.
B. Provide the first leaves.
C. Hydrolyze the food in the endosperm.
D. Protects the plumule.
20. A mammalian embryo exchanges materials with its mother by
A. Osmosis.
B. Secretion.
C. Circulation.
D. Diffusion.
21. Which one of the following statements is the most appropriate definition of respiration?
A. The oxidation of sugar to produce energy and water.
B. Breathing in oxygen, oxidation of food and release of water, carbon dioxide and energy.
C. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
D. The oxidation of sugar to produce carbon dioxide and energy.
22. 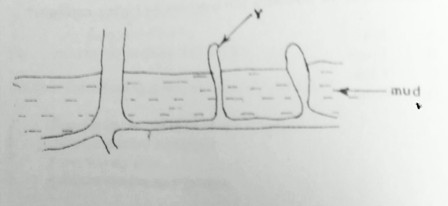
The root modification shown by Y on page 5 is for
A. Storage.
B. Excretion.
C. Breathing.
D. Extra support.
23. In what part of the green flowering plant does meiosis occur?
A. Seed
B. Flower
C. Fruit
D. Shoot apex
24. A bat is classified as a mammal because
A. It does not possess feathers.
B. It has specialized teeth.
C. It has four limbs.
D. Its digits have claws.
Study the web below and use it to answer questions 25 and 26.
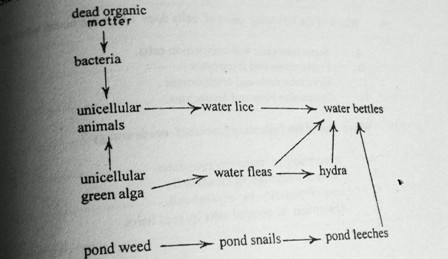
25. In this food web, which of the following groups of organisms are primary consumers?
A. Pond leeches and water fleas.
B. Pond snails and unicellular animals.
C. Hydra and water beetles.
D. Bacterial and water fleas.
26. In this food web which one of the following groups of organisms are decompress?
A. Unicellular green algae
B. Water beetles
C. Water lice
D. Bacteria
27. Which one of the following features is typical of the class insect?
A. Jointed legs.
B. Three body parts.
C. Complete metamorphosis.
D. Exoskeleton
28. Which one of the following types of feathers is most widespread?
A. Covert feather.
B. Filiplumes.
C. Quill feathers.
D. Down feathers.
29. Which of the following pairs of cells does not have nuclei when mature?
A. Sieve tube cells and companion cells.
B. Erythrocytes and leucocytes.
C. Sieve tube cells and crythrocytes.
D. Companion cells and leucocytes.
30. Which one of the following processes needs energy?
A. Absorption of water by root hairs.
B. Gaseous exchange in the alveoli.
C. Loss of turgidity by a plant cell.
D. Absorption of mineral salts by root hairs.
SECTION B
Answer all questions in this section. Answer must be written in the spaces provided.
31. a) (i) What is meant by the term mutation?
b) The gene for normal production of hemoglobin is dominant to the mutant gene which causes sickle cell anaemia. If a female heterozygous for the sickle cell anaemia marries a normal man, illustrate, using suitable symbols, the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring.
32. a) Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands.
b) Below is a diagram of a human female showing the location of two endocrine glands.
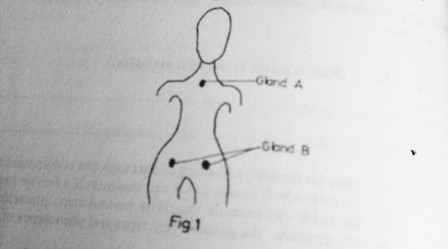
Name the glands A and B and one hormone produced by each.
c) Give three effects of adrenaline in the body.
33. Figure 2 (a) shows a vertical section of the end region of a growing root and figure 2 (b) shows an enlargement of a cell from the root.
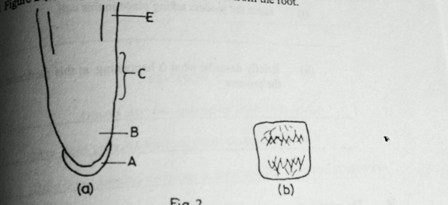
a) (i) Name the region labelled A
(ii) How does growth occur in the region labelled B?
(iii) Describe briefly what happens to the cells in the region labelled C.
(iv) What structures might be expected to grow at the region marked D?
b) State the function of region marked A.
c) Figure 2 (b) shows a cell from region B.
(i) Name the process taking place in the cell.
(ii) Briefly describe what is happening at this particular stage of the process.
34. The graph below shows the relationships between body temperatures and external temperatures in human being and a lizard.
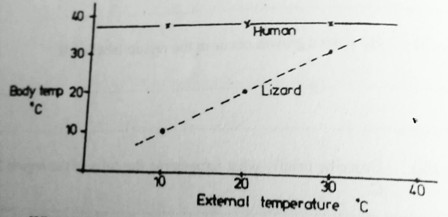
a) What happens to the temperature of each organism as the external temperature increases?
Human.........................................................................................................
Lizard ...........................................................................................................
b) Humans are sometimes described as warm-blooded (homoiotheric). State the advantage of this condition.
c) Suggest how a lizard living in hot desert conditions might avoid overheating if external temperatures rose above 400c.
SECTION C
Answer any two questions from this section.
35. a) How does gaseous exchange take place in an insect?
b) How does gaseous exchange in insects differ from that in mammals?
36. Describe an experiment you would carry out to test for the presence of starch in a leaf.
37. a) Draw a well labelled diagram of a human female reproductive system.
b) Outline the events that lead to the fertilization of the ovum in the human female.
38. a) Describe the structure of a motor neuron.
b) (i) What is meant by reflex action?
(ii) By means of a diagram, show the path followed by a nerve impulse during a reflex action.
