SECTION A
1. An alkene R, diffuses through a porous partition in 2 minutes. Under similar conditions, the same volume of oxygen diffuses in 1.75minutes.
a) i) Calculate the formula mass of R.
ii) Determine the molecular formula of R.
b) Write equations to show how R can be synthesized from propanone.
2. a) In the manufacture of sulphuric acid, sulphur trioxide is not dissolved in water, bit another solvent.
i) State why water is not used as a solvent
ii) Write equation(s) to show the formation of sulphuric acid from sulphur trioxide.
b) Write equation for the reaction between sulphuric acid and hydrogen bromide.
3. a) Complete the following equations for nuclear reactions.
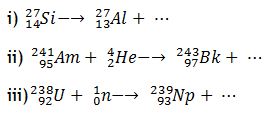
b) In an experiment, the rate of radioactive decay of bromine decreased by 25% in 96 minutes. Calculate the half life of bromine.
4. a) State one colligative property of dilute solution other than depression of freezing point or elevation of boiling of a solvent.
b) Ethane -1-2 dio HOCH2CH2OH, is used as an antifreeze for water in car radiators. Calculate the mass of ethane -1-2- diol that should be added to 1 kg of water prevent it from freezing at -100C.
(Freezing point depression constant for water = 1.860C kg mol-1)
5
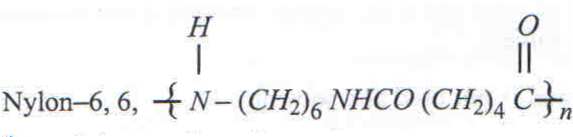 is a synthetic polymer formed by condensation polymerisation.
is a synthetic polymer formed by condensation polymerisation.
a) State what us meant by the term condensation polymerisation
b) Write the structural formulae of the monomers of nylon -6, 6.
c) Name:
i) one natural polymer that us formed by condensation polymerisation.
ii) the monomers of the polymer in (c) (i).
d) State one use of the polymer you have named in (c) (i)
6. a) State two properties in which chromium behaves as a transition element.
b) Write the equation for the reaction that takes place when chromium (III) sulphate is dissolved in water.
c) Magnesium ribbon was added to a solution of chromium (III) sulphate.
i) State what was observed.
ii) Write the equation for the reaction that took place.
7. Explain the following observations:
a) Silicon (IV) chloride is hydrolysed by water whereas carbon tetrachloride is not.
b) Lead(IV)chloride exists but lead(IV) bromide does not.
8. The graph below shows how total vapor pressure of a mixture of water and nitrobenzene varies with temperature.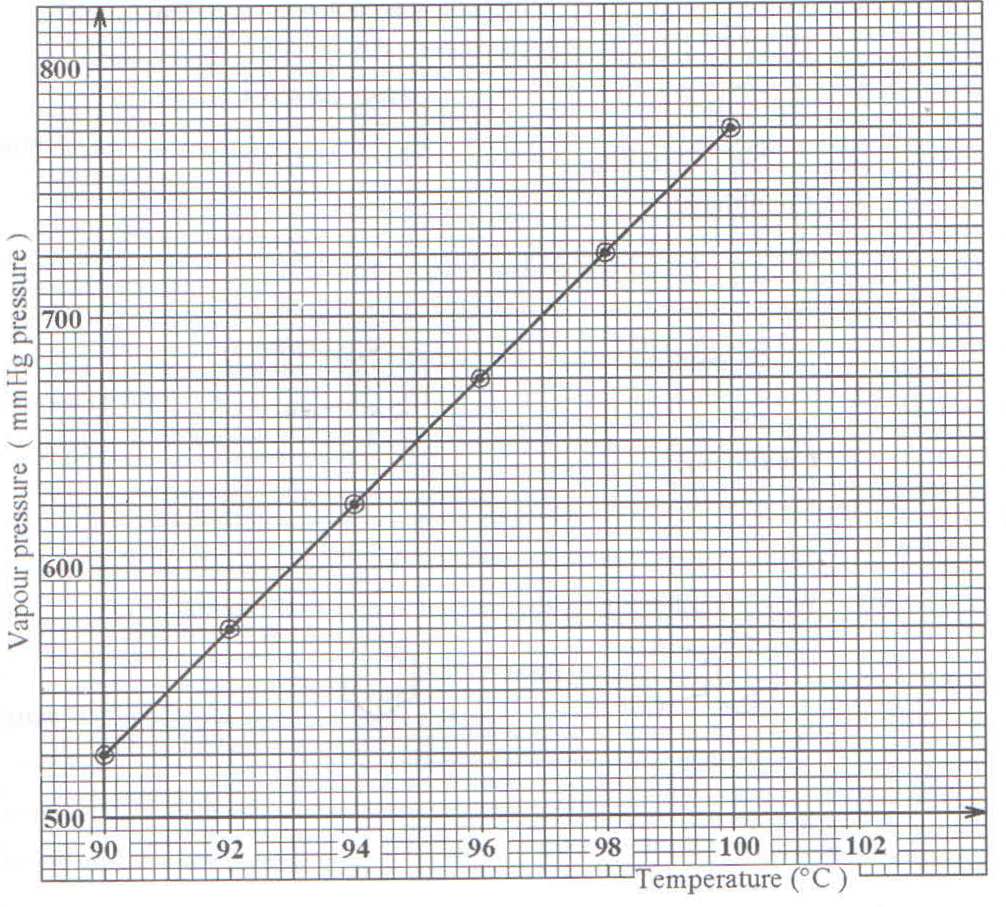
a) State the temperature at which the mixture boils at 760mmHg pressure.
b) The partial vapor pressure of nitroobenze at the boiling point of the mixture is 20mm Hg. Calculate the percentage of nitrobenzene by mass that will be obtained when the mixture is steam distilled at normal atmospheric pressure. (H =1; C =12; N=14; O=16)
9. a) State the condition(s) under which the following conversions can be effected.
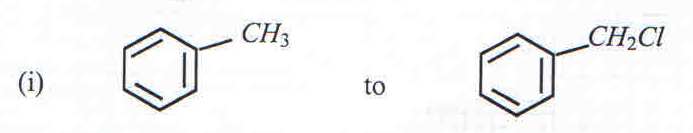
Conditions
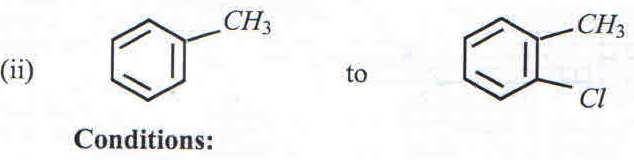
b) Write a mechanism for the reaction leading to the formation of

SECTION B
Answer six questions from this section
10. Complete each of the following equations and write the mechanism for the reaction.
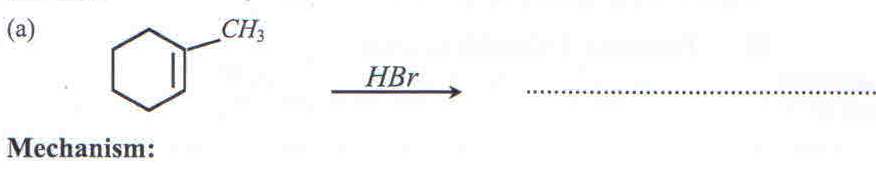
CH3CH2NH2
b) CH3COBr --------------------->
Heat
Mechanism:
KCN/H+
c) HCHO------------>
Mechanism:
11. a) State what us meant by the term buffer solution
b) Calculate the pH of the solution formed when 0.61g of benzoic acid is dissolved in 1 dm3 of a 0.02M sodium benzoate.
(Ka of benzoic acid = 6.3 x 10-5 mol dm-3)
c) Explain what would happen to the pH of the solution in (b) if a few drops of the following reagents were added:
i) Potassium hydroxide solution
ii) Hydrochloric acid.
12. a) When 0.1g of aluminum chloride was vaporized at 3500C and pressure of 1 atmosphere, 19.2cm3 of vapor was formed.
i) Calculate the relative molecular mass of aluminum chloride.
ii) Write the molecular formula of aluminum chloride in the gaseous state at 3500C. (Al = 27; Cl =35.5).
b) Aluminum chloride is normally contaminated by traces to iron (III) chloride.
i) Name one reagent that can be used to detect the presence of iron (III) ion in a contaminated solution of aluminum chloride.
ii) State what would be observed if the contaminated aluminum chloride solution was treated with the reagent you have named in (b) (i).
iii) Write equation for the reaction leading to the observation you have stated in (b) (ii)
c) Water was added drop wise to aluminum chloride.
i) State what was observed
ii) Write equation for the reaction that took place.
d) State one use of aluminum chloride in organic synthesis.
13. a) Draw the structure and name the shape of each of the species in the table below.
|
Species |
Structure |
Shape |
|
BF3 |
||
|
SnCl2 |
||
|
ClO3- |
b) Write equation for the reaction between:
i) boron trifluoride and ammonia
ii) acidified potassium iodide solution and aqueous sodium chlorate (V) solution
iii) tin(II) chloride and iron(III) ions.
14. a) Write:
i) equation for the ionization of methanoic acid in water.
ii) the expression for the acid dissociation constant Ka, for methanoic acid.
a) The molar conductivities of some electrolytes at infinite dilution at 250C are given in the table below.
|
Electrolyte |
Molar conductivity at infinite dilution (Scm2 mol-1) |
|
Sodium chloride |
113.0 |
|
Sodium methanoate |
101.0 |
|
Sodium hydroxide |
225.2 |
|
Hydrochloric acid |
397.8 |
Calculate the molar conductivity of methanoic acid at infinite dilution
c) The molar conductivitu of a 0.05M methanoic acid solutionis 24.318 Scm2 mol -1 at 250C.
Calculate the:
i) degree of ionization of methanoic acid at 250C
ii) dissociation constant Ka of methanoic acid at 250C
15. Name one functional group that can be identified using each of the following reagents. In each case state what would be observed and write equation for the reaction that would take place:
a) Bromine water
Functional group:
Observation
Equation:
b) 2,4 – dinitrophenyl hydrazine.
Functional group:
Observation
Equation:
c) Sodium carbonate
Functional group:
Observation
Equation:
16. During the extraction of copper from copper pyrites, copper pyrites is crushed and agitated with water/oil mixture. Compressed air is bubbled through the mixture which is then filtered, roasted and finally impure molten copper is obtained.
a) State the role of
i) oil
ii) compressed air
b) Write equation for the reaction that occurs when copper pyrites is roasted.
c) Explain briefly how impure copper can be refined.
d) Explain why it is advantageous to have a sulphuric acid manufacturing plant near a copper extraction plant.
17. a) State what is meant by the term:
i) order of a reaction
ii) Half life of a reaction
b) The table below shows the kinetic data obtained for hydrolysis of methyl ethanoate in acidic media.
|
[CH3COOCH3] (mol dm-3) |
0.241 |
0.161 |
0.109 |
0.073 |
0.046 |
0.034 |
|
Time (minutes) |
0 |
60 |
120 |
180 |
240 |
320 |
Ploton a graph of concentration of methyl ethanoate against time.
c) Using the graph in (b) determine the:
i) half life of the reaction.
ii) order of the reaction with respect to CH3COOCH3. Give a reason for your answer.
e) Calculate the rate constant and indicate its units.