PAPER 1
SECTION A
Answer all questions section
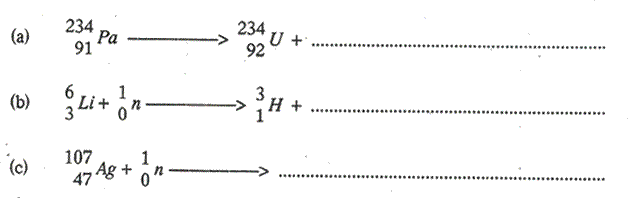
1. Complete the following equations:
2. (a)Oxygen diffuses 1.19 times faster than an amine Q.
(i)Determine the relative molecular mass of Q
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii)Write the structural formulae of all possible isomers of Q
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)When Q was reacted with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at 00C, nitrogen gas was evolved and a colorless solution was formed
Identify Q.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3. Substance X dissolved in water to form a yellow solution. When aqueous sodium hydroxide was added drop wise to the solution, a brown solid insoluble in excess alkali was formed.
(a) (i) Identify the cation in X.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)Name one reagent that can be used to confirm the cation you have identified in (i).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)The pH of the solution of X was less than 7
Explain the observation and write an equation to illustrate your answer
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
4. A 0.01M solution of ammonia is 4.0% ionized.
(a)Calculate the pH of the solution (Kw = 1x10-14)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Determine the base dissociation Kb for the ammonia solution
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
5. Compound B was synthesized according to the reaction scheme shown below.
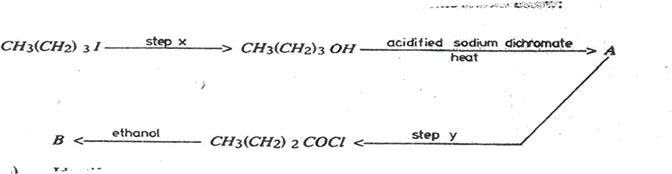
(a)Identify the reagents in
(i) step x
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) step y
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) state the conditions for the reaction in
(i) step x
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) step y
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Write the name and structural formula of compound
(i)A
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)B
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
6. When excess zinc was added to 100cm3 of 0.25 copper (II)sulphate solution the temperature of the solution rose by 12.90C.
(the specific heat capacity and density of the solution are 4.2jg-1K-1 and 1.0g cm-3 respectively)
(a)Write an equation for the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
7. (a)Write the electronic configuration of strontium.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)What is the principal oxidation state of strontium?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) State whether the first ionization energy of strontium is greater or less than that of barium. Explain your answer
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
8. (a)Explain what is meant by steam distillation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)A mixture of naphthalene (C10H8) and water distils at 98.30C and 753mmhg
Calculate the percentage by mass of naphthalene in the distillate
(the vapor pressure of water at 98.30C is 715 mm Hg)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
9. Name one reagent that can be used to distinguish between each of the following compounds. In each case state what would be observed if each member of the pairs is treated with the reagent.
(a)CH3COOH and HCOOH
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….

…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
SECTION B
Attempt six questions from this section.
10. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation.
N2 (g) + 3H2(g)⇄2NH3(g)
(a) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for the reaction in terms of partial pressure and indicate its units
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Stoichiometric amounts of nitrogen and hydrogen were reacted at 50 atmospheres and at equilibrium, 0.8 moles of ammonia was formed
Calculate
(i)the amount of hydrogen at equilibrium
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)The value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
11. Write equations to show how each of the following can be synthesized. In each case indicate the conditions for the reaction.
(a)CH3CH2NH2 (from CH3CH2COOH)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
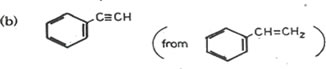
![]()
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
12. Name one reagent that can be used to distinguish between each of the following pairs of ions and in each case what would be observed.
(a)Mg2+ and Ca2+
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Cl- and I-
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) CO2-3 and HCO-3
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
13. The data in the table below was obtained for the reaction.
|
Time (hours) |
0 |
1.3 |
2.0 |
4.0 |
5.3 |
|
Log10(A) |
-0.07 |
-0.24 |
-0.33 |
-0.57 |
-0.74 |
(a)Plot a graph of log 10(A) against time.
(b)From the graph determine the order of the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c)Calculate
(i)the rate constant for the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)the half life of the reaction
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
14. Complete each of the following equations and write a mechanism for the reaction.
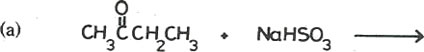
Mechanism:
![]()
Mechanism:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Mechanism:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
15.1.55g of an acid CnH2n(COOH)2 was dissolved in water made up to 250cm3.25.0cm3 of the solution required 23.5cm3 of a 0.1M aqueous sodium hydroxide for complete neutralization.
(a) Calculate
(i)the molar concentration of the acid
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)the molar mass of the acid
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Determine the value of n
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c)Write the structural formula of the acid
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
16 (a) The curve below was obtained when hydrochloric acid was titrated with sodium hydroxide.
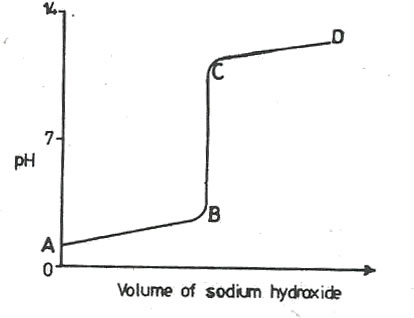
Explain what happens to the pH in the region
(i)AB
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii)BC
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii)CD
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b)Name one indicator that can be used in the titration in (a)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Using the axes above, sketch a graph that would be obtained if hydrochloric acid is titrated with ammonia solution.
17. (a)In volumetric estimation of reducing agents, potassium dichromate(VI) is preferred to potassium manganate(VII) as an oxidant.
Explain why potassium dichromate (VI) is preferred as an oxidant
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) 3.8g of solder containing tin was dissolved in excess hydrochloric acid. The solution was made up to 250cm3.25.0cm3 of this solution required 23.5cm3 of a 0.01M potassium dichromate (VII) solution for complete reaction
(i)Write the half equation for potassium dichromate (VI) acting as an oxidizing agent in acid medium
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Calculate the number of moles of potassium dichromate (VI) used
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Calculate the number of moles of tin in 25ocm3 of solution
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) Determine the percentage by mass of tin in the solder
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
1.
2.
PAPER 2
SECTIONA
Answer five questions including three questions from section A and any two from section B.
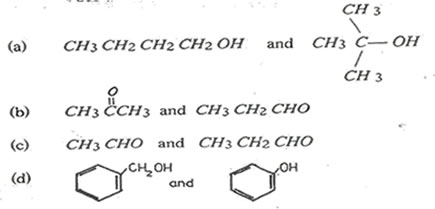
1. For each of the following pairs of compounds name one reagent that can be used to
(i)test for functional group
(ii)distinguish between each of the pairs
Your answer should include the relevant observation
2. (a) State Raoult`s law.
(b)A mixture of liquids A and B obeys Raoult`s law. The vapour pressure of A and B are 10.00kN m-2 and 2.92kNm-2 respectively at 200C.
(i)Calculate the composition of the vapour of a mixture containing 0.5 mol of each liquid at 200C.
(ii) Which of the liquids is more volatile? Give a reason for your answer.
(c) The diagram below shows the boiling point composition of a mixture of liquids X and Y
(i)Identify the curves P and Q and the points M and N.
(ii)Describe what happens when the liquid mixture of composition Z is boiled.
(iii)Explain how the principal in (ii) can be used to separate liquid mixtures by fractional distillation.
3. (a) Describe one general method for preparing halogens(excluding fluorine) in the laboratory and write an equation for the reaction.
(b) Describe the reactivity of fluorine chlorine and bromine with
(i) water
(ii) concentrated sodium hydroxide solution
Your description should include equations
(c)How would you distinguish between sodium bromide and sodium iodide given chlorine water and tetrachlromethane?
4. (a) Describe how the solubility product of magnesium hydroxide in water can be determined.
(b) (i) A saturated solution of magnesium hydroxide in water contains 1.44x10-4 mol of magnesium hydroxide per litre of solution at 250C.calculate the value of the solubility product, Ksp of magnesium hydroxide at 250C.
(ii)Solid magnesium hydroxide was shaken with a 0.1M solution of magnesium nitrate until equilibrium was attained at 250C.
Calculate the amount of magnesium hydroxide in grams per litre that dissolved.
(c)Equations for some reactions are given below:
AgCl(s) ⇄ Ag+ (aq) + Cl-(aq) K1=1.7x10-10
Ag+ (aq) + 2NH3 (aq) ⇄ Ag (NH3)2+(aq) K2 =1.7x107
(i) Derive an expression in terms of K1 and K2 for the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
AgCl(s) + 2NH3 (aq) ⇄ Ag (NH3)2+ + Cl-(aq)
(ii) Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant in (i)
SECTION B
5. (a) (i) Explain what is meant by the term lattice energy.
(ii) State two factors that affect the magnitude of lattice energy.
(b) (i) Draw a Born-Haber cycle for the formation of solid rubidium chloride from its elements
(ii)Calculate the electron affinity of chlorine atom.
Use the following data:
Lattice energy of rubidium chloride =665kjmol-1
Dissociation energy of chlorine gas molecules =226 kjmol-1
Heat of atomization of rubidium metal =84 kjmol-1
Ionization energy of rubidium atom =397 kjmol-1
Standard heat of formation of solid rubidium chloride =-439 kjmol-1
(c) Calculate the heat of hydrogenation of ethyne to ethene from the following thermodynamic data:
6. Write notes on each of the following. Your answer should include suitable example I each case and also mechanisms for reactions (a) and (d).
(a) Nucleophilic substitution
(b) Nitration
(c) Esterification
(d) Dehydration of alcohols.
7. (a) (i) Write an name the formula of one ore of zinc.
(i) Briefly describe how pure zinc can be obtained from the ore you have named in (i)
(b) (i) Name one reagent that can be used to distinguish between zinc ions and aluminium ions in solution.
(ii) State what would be observed when zinc and aluminium ions are separately treated with the reagent. Write equations for the reactions.
(c) Explain how zinc protects iron from rusting
8. Explain each of the following observations:
(a) The boiling point of trimethaylamine,(CH3)3N is less than that of dimethylamine,(CH3)2NH.
(b) 0.01M aqueous sodium chloride has the same freezing point as 0.02M aqueous glucose.
(c) Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.
(d) Copper (II) chloride dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric acid to form a brownish yellow solution which on dilution with water turns green blue and finally pale blue.
